Zero knowledge proof (ZKP) is rapidly becoming one of the most important technologies in modern blockchain development. As decentralized networks grow, the need to verify transactions and data without exposing sensitive information has become critical. Zero knowledge proof (ZKP) enables exactly that—allowing one party to prove a statement is true without revealing the underlying data. This article explains how ZKP-based crypto projects work, why the technology matters, and how it delivers real-world value while maintaining transparency, security, and scalability across blockchain ecosystems.
Project Overview: What a Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) Crypto Project Does
A crypto project built around zero knowledge proof (ZKP) focuses on validating transactions, identities, or computations while preserving privacy. Instead of placing all transaction details on-chain, the project uses cryptographic proofs to confirm correctness without revealing private information.
ZKP-based platforms are widely used in Layer-2 scaling solutions, privacy-focused blockchains, decentralized finance applications, and identity verification systems. The main objective is to reduce on-chain data load while increasing trust and efficiency. By leveraging zero knowledge proof (ZKP), these projects allow public blockchains to remain transparent and verifiable without compromising user confidentiality.
How Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) Technology Works
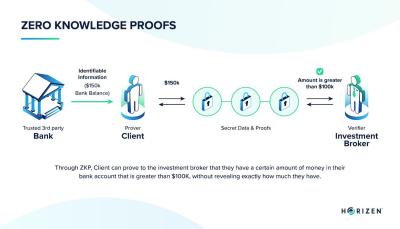
To understand zero knowledge proof (ZKP), imagine proving that you know a secret without ever revealing the secret itself. In blockchain systems, this means proving a transaction is valid without showing transaction details.
The process involves two parties: a prover and a verifier. The prover generates a cryptographic proof using mathematical algorithms, while the verifier checks the proof against predefined rules. If the proof is valid, the transaction or computation is accepted.
Most ZKP-based crypto projects rely on zk-SNARKs or zk-STARKs. zk-SNARKs are lightweight and efficient but often require a trusted setup phase. zk-STARKs remove the need for trusted setup and offer better scalability, though they demand higher computational resources. Both methods allow complex computations to be verified on-chain using small, efficient proofs.
Key Features and User Benefits of Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP)
Zero knowledge proof (ZKP) offers clear advantages that directly benefit users and networks.
Privacy is the most obvious benefit. Transaction values, wallet balances, and personal data remain hidden while still being verifiable. This makes blockchain technology more suitable for enterprise and institutional use.
Scalability is another major advantage. Since most computations occur off-chain, blockchain congestion is reduced. This leads to faster transaction processing and lower fees.
Security is also strengthened. Sensitive data is never published on-chain, minimizing exposure to attacks and data leaks.
Finally, zero knowledge proof (ZKP) enables selective disclosure. Users can prove compliance or eligibility without revealing full datasets, supporting regulatory-friendly blockchain adoption.
Tokenomics: Supply, Distribution, and Utility
Transparent tokenomics play a key role in the credibility of any zero knowledge proof (ZKP) crypto project. Most projects define a fixed or capped token supply to prevent inflation and protect long-term value.
Token distribution is typically divided among ecosystem growth, development funding, validator incentives, community rewards, and early supporters. Vesting schedules are commonly applied to ensure sustainable participation and prevent market manipulation.
In terms of utility, the token is often used to pay network fees, stake for proof generation or validation, participate in governance, and access advanced privacy features. In some ecosystems, proof generators must lock tokens as collateral, aligning incentives and discouraging malicious behavior.
Practical Use Cases of Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP)
Zero knowledge proof (ZKP)
technology is already solving real problems in the blockchain space. In decentralized finance, ZKP enables private trading, confidential lending positions, and hidden collateral balances without compromising trust.
In blockchain scaling, ZKP powers rollups that bundle thousands of transactions into a single proof, significantly improving throughput and reducing costs. Identity platforms use zero knowledge proof (ZKP) to allow users to verify credentials such as age or residency without revealing personal information.
Supply chain systems apply ZKP to verify authenticity, compliance, and data accuracy while protecting proprietary business information. Governance and voting platforms rely on ZKP to ensure fair, anonymous participation without double voting or manipulation.
Advantages and Challenges of Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) Projects
The advantages of zero knowledge proof (ZKP) are substantial. Privacy, scalability, security, and regulatory flexibility make it one of the most powerful tools in blockchain innovation.
However, challenges remain. ZKP systems are technically complex and require advanced cryptographic expertise. Proof generation can be computationally intensive, especially for consumer devices. Some implementations also raise concerns around trusted setup and decentralization.
Reliable projects address these issues through open-source development, third-party audits, hardware optimization, and gradual protocol upgrades that improve performance over time.
Roadmap and Long-Term Development Goals
A strong zero knowledge proof (ZKP) project follows a realistic and transparent roadmap. Early milestones usually include testnet launches, proof system optimization, and security audits. Mid-term goals often focus on mainnet deployment, ecosystem partnerships, and developer tooling.
Long-term development typically aims at cross-chain interoperability, improved proof efficiency, and broader adoption across industries. Clear milestones, frequent updates, and measurable progress help establish long-term credibility and trust.
Conclusion
Zero knowledge proof (ZKP) is redefining how trust, privacy, and verification function in blockchain ecosystems. By enabling validation without data exposure, ZKP-based crypto projects unlock scalable, secure, and privacy-preserving decentralized applications. When combined with transparent tokenomics, real-world use cases, and a realistic roadmap, zero knowledge proof (ZKP) stands as a foundational technology shaping the future of blockchain innovation.